On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), often referred to as the “Bipartisan Infrastructure Law” (BIL), was signed into law. With the BIL’s passage, the United States has committed approximately $550 billion to transportation infrastructure within a wider $1 trillion + federal reinvestment in the nation’s infrastructure [1].
Much of the BIL transportation funding seeks to encourage and prioritize the repair, reconstruction and replacement and maintenance of existing transportation infrastructure with appropriations totaling some $350.8 billion (FY 2022-2026), drawing from the highway trust fund ($303.5 billion) and advance appropriations from the general fund (47.3 billion). Most of the highway funding is apportioned to States based on formulas specified in Federal law. New Jersey could receive approximately $8.1 billion over five years for highways and bridges, based on the federal highway funding formula, or about 41.6 percent more than the State’s funding under current law [2]. However, the BiL also provides significant funding through various competitive grant programs such as the bridges and megaprojects that can demonstrate substantial economic benefits. New Jersey’s Portal North Bridge under construction in Secaucus reportedly may meet the requirements for a Capital Investment Grant for transit projects [2].
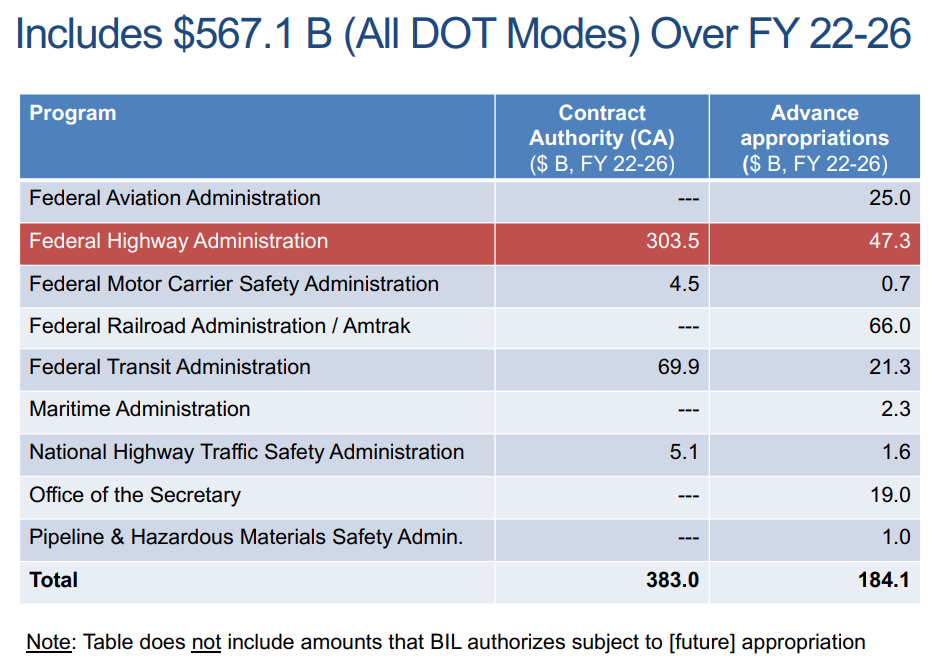
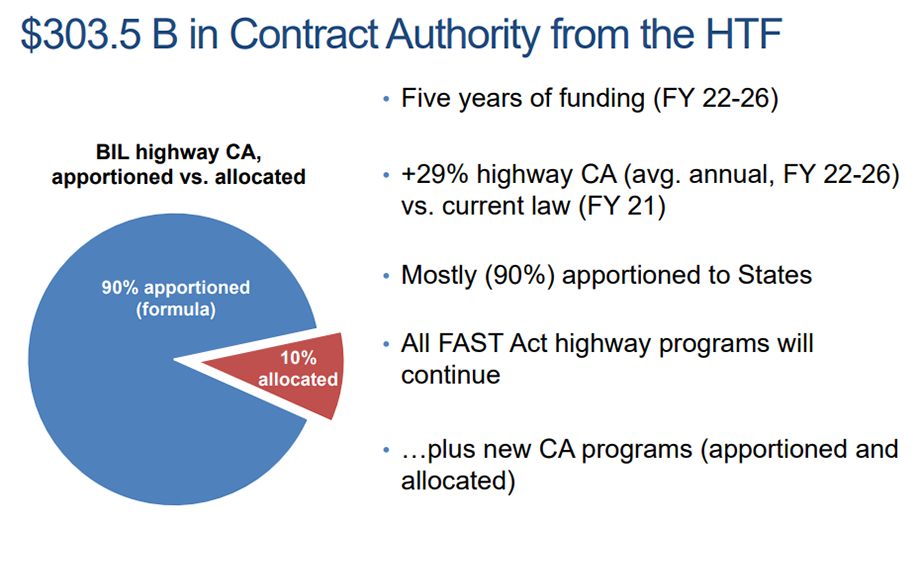
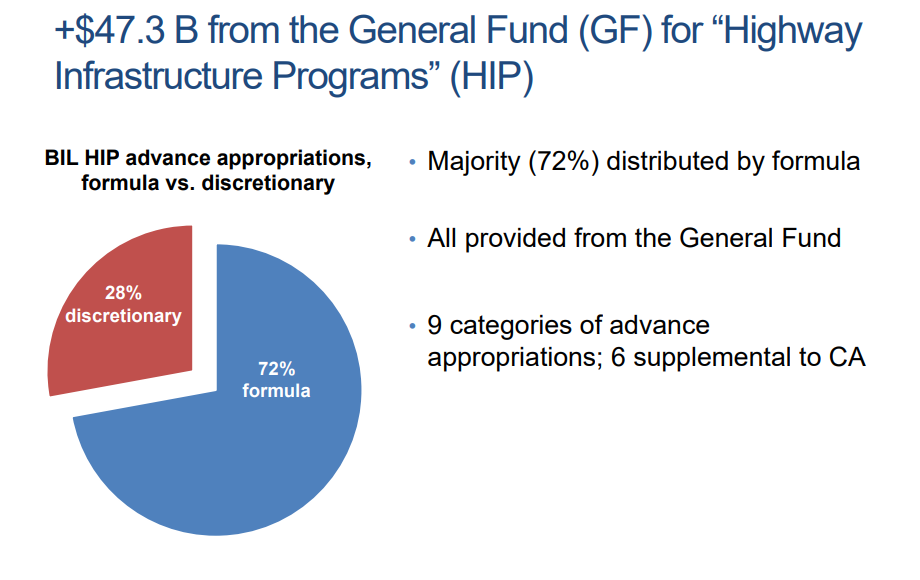
Notably, the BIL takes innovative steps in the realms of safety, equity, and climate change and resilience to increase investment and resources for programs, new and old, that will tackle the challenges of the 21st century in both a national and New Jersey-specific context. Growing awareness of the broad harms of road hazards, inequity and injustice, and climate change will inform not only the purpose of specific program investments but influence transportation planning, project delivery, and research for years to come.
Safety
A major program that will advance safety innovation and renovations across the country is the $5 billion, FY 2022-2026 Safe Streets for All (SS4A) Program. A “Complete Streets” program, SS4A is a discretionary program which seeks to advance USDOT’s goal of zero deaths and serious injuries on our nation’s roadways by implementing multi-modal improvements and safety treatments. Examples of applicable SS4A modifications include separated bicycle lanes, traffic calming road design changes, rumble strips, wider edge lines, flashing beacons, and better signage. Metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs), local, and tribal governments are eligible to apply for this funding. Separate provisions in BIL define Complete Streets standards and policies. Additional information on SS4A can be found here. FHWA provides accessible information on Complete Streets here.

Changes have been made to existing safety programs such as the Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP) which could prove to more holistically mitigate road hazards. Eligibility for HSIP’s funds (up to 10 percent) can now be used for “specified safety projects (including non-infrastructure safety projects related to education, research, enforcement, emergency services, and safe routes to school)” [1]. Definitions for the program have been modified to recognize as eligible a variety of new types of projects such as traffic control devices for pedestrians and bicyclists and “roadway improvements that separate motor vehicles from bicycles or pedestrians” [1]. State-level assessments of vulnerable road users are rolled into the requirements of the HSIP. More information on these guidance changes can be found here.
Funding for highway safety traffic programs under the BIL are $13 billion more than the levels established for the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation (FAST) Act. In FY2022-2026, 402 formula funding for highway safety traffic programs is expected to allocate approximately $42 million to New Jersey to help improve driver behavior and reduce deaths and injuries from motor vehicle-related crashes. This funding represents about a 29 percent increase over FAST Act levels [2] when averaged on an annual basis. Such increases in funding for roadway safety improvement provides an opportunity to put forward educational, enforcement and design strategies to counter a recent surge in US and NJ traffic fatalities.
Equity
To promote and implement equity-oriented innovation, the current administration has held itself to a “Justice40 commitment,” the goal of which is to deliver 40 percent of the benefits of the climate and energy related investments to disadvantaged communities [3]. This commitment is reflected in BIL’s transportation funding. One example provided by USDOT is that $5.6 billion in Low- or No-Emission Bus Grants to transition to low- or zero-emission buses will be assessed and likely partially directed to low-income communities to advance environmental justice.
USDOT developed a definition for disadvantaged communities (DACs) to be utilized in connection with certain criteria under Justice40-covered grant programs. The DAC definition draws upon data for 22 indicators collected at the U.S. Census tract level, which are then grouped into six categories of transportation disadvantage to identify places that are disadvantaged.
The Justice40 Disadvantaged Community Interim Definition goes as follows:
- Transportation access disadvantage identifies communities and places where residents spend more, and take longer, to get where they need to go.
- Health disadvantage identifies communities based on variables associated with adverse health outcomes, disability, as well as environmental exposures.
- Environmental disadvantage identifies communities with disproportionately high levels of certain air pollutants and high potential presence of lead-based paint in housing units.
- Economic disadvantage identifies areas and populations with high poverty, low wealth, lack of local jobs, low homeownership, low educational attainment, and high inequality.
- Resilience disadvantage identifies communities vulnerable to hazards caused by climate change.
- Equity disadvantage identifies communities with a high percentile of persons (age 5+) who speak English "less than well."
To assist grant applicants in identifying whether a proposed project is located in a DAC, USDOT provides a list of U.S. Census tracts that meet the DAC definition and a corresponding mapping tool, Transportation Disadvantaged Census Tracts (Historically Disadvantaged Communities).
Several USDOT programs are using the interim definition of DACs to ask discretionary grant applicants and formula program administrators to identify how their projects benefit DACs. More information on how the Justice40 commitment shapes the equity orientation of BIL’s transportation funding can be found here.
One major new BIL program addressing inequities within America’s transportation infrastructure is the Reconnecting Communities Pilot Program. The discretionary program was conceived to provide $1 billion over five years to remedy the negative effects of past transportation investment decisions that divided communities [1], such as highway expansions that cut cities in half. Applicants for Reconnecting Communities funding can seek capital constructions grants (such as for the replacement of an eligible facility with a new facility that restores community connectivity) or as well as planning grants and technical assistance grants. More information about this innovative program to redress the adverse cumulative effects borne by communities from past transportation investments can be found here.
For New Jersey, the Reduction of Truck Emissions at Port Facilities Program is another innovative program that holds promise for redressing the environmental health effects attributable to siting and operating regional goods movement facilities. By funding the study of, and competitive grants to reduce, truck idling and emissions at ports (such as promotion of port electrification and possibly hydrogen-fuel technologies), pollutants and adverse health disparities borne by port communities could be reduced. Northern New Jersey, as one of the most important freight hubs in North America, is likely to receive some of the $400 million available in discretionary funding (FY2022-FY2026) as well as a portion of the Port Infrastructure Development Program’s annual budget, recently increased to $450 million. These investments to modernize and reduce the environmental burdens of the nation’s freight infrastructure could reduce unfairly distributed health hazards in New Jersey.
In line with the Justice40 commitment, a number of regulatory changes to existing programs contain equity-oriented provisions. In the continuation of the Fixing America's Surface Transportation (FAST) Act, the Metropolitan Planning Program has a BIL requirement “to consider equitable and proportional representation of population of metropolitan planning area when the MPO designates officials or representatives” [1]. Such requirements, even when non-binding, support a wider culture and consideration of equity in how the nation’s urban and transportation policies are devised and implemented. Many communities today live with the legacy of decisions made without their input, and so this innovative provision in the Metropolitan Planning Program is an appropriate step to discontinue such inequities in institutional processes.
Climate & Resilience
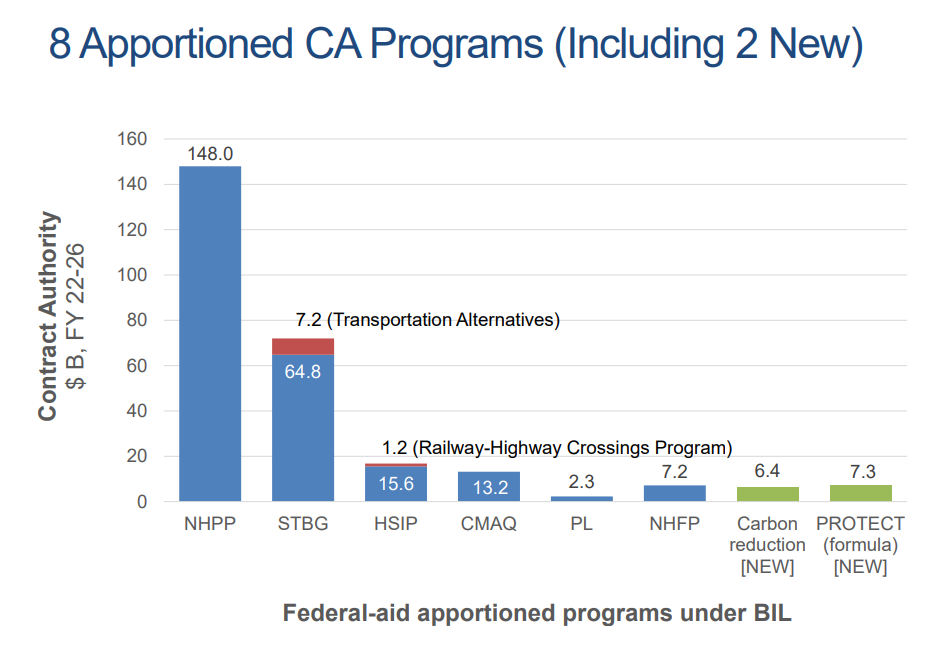
The climate and resilience orientation of the BIL presents innovation not only in fashioning new programs but in integrating carbon reduction goals into existing infrastructure funding frameworks. The newly established Carbon Reduction Program is a formula-funded $6.4 billion addition to the Highway Trust Fund (HTF) for the purpose of backing projects that reduce transportation emissions, and support development of broader carbon reduction strategies. Projects as varied as congestion pricing systems, infrastructure for alternative fueled vehicles (electric, hydrogen, propane, and natural gas), port electrification, replacement of street lighting and traffic control devices with energy-efficient alternatives, and public transportation are eligible. Additional information on the Carbon Reduction Program can be found here.
Increased need for disaster resiliency in transportation systems informs the purpose of the newly established Promoting Resilient Operations for Transformative Efficient, and Cost-saving Transportation (PROTECT) program. Like the Carbon Reduction Program, PROTECT injects $7.3 billion in the HTF for a formula distribution to the states and also provides $1.4 billion in discretionary funds. This $8.7 billion will help fund resilience improvements in highways, transit systems, intercity passenger rail, and port facilities, as well as support the development of resiliency and evacuation plans. For FY2022 alone, New Jersey is expected to receive roughly $34 million [4] from PROTECT, presenting the opportunity to proactively guard the State’s transportation system from hazards related to climate change. Discussion from the National League of Cities on PROTECT can be found here.
Within the realm of innovative transportation technology, the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program seeks to expand the supply of infrastructure to support the growing presence, if not the transition, of the nation’s fleet to electric and alternative fuel vehicles. Providing approximately $5 billion over five years, NEVI is designed to establish Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations “along designated Alternative Fuel Corridors, particularly along the Interstate Highway System.” Building on existing federal plans such as Alternative Fuel Corridors, NEVI seeks to guarantee interstate travel by electric vehicle nationally.
Given that New Jersey has the highest number of electric cars per charging station of any state in the country, this additional push is well-suited to the state’s needs and climate goals. The NEVI formula is expected to provide New Jersey with $104.4 million; at an estimated cost per station of $173,000, this level of investment would pay for around 600 charging stations [5]. This funding represents 2.5 percent of the total fund which is roughly commensurate with New Jersey’s Census 2020 population share of 2.8 percent. Another $1.4 billion is available through NEVI discretionary funding that New Jersey could compete to receive.
Similarly, the discretionary Charging and Fueling Infrastructure Program is a competitive funding program with $2.5 billion available to implement innovative fueling infrastructure. At least fifty percent of this funding must be used for a community grant program that prioritizes projects in rural areas, low- and moderate-income communities, and communities with a low ratio of private parking spaces. New Jersey governments’ ability to compete for this funding could shape the built environment and advance the state’s carbon reduction goals for years to come.
Additional information on the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program can be found here. Additional information on how NEVI and the Charging and Fueling Infrastructure program connect within new federal funding programs for EV Charging can found here. An article of NEVI’s role in New Jersey can found here.

Conclusion
These new and innovative programs and provisions of the BiL focus on safety, equity, climate change and resilience topics. However, the BiL’s highway provisions establish funding and make changes to numerous other programs focused on the nation’s continuing infrastructure, congestion, safety, community, environmental and project delivery challenges. The Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality (CMAQ) Improvement Program, the Surface Transportation Block Grant (STBG) Program, the National Highway Freight Program (NHFP), the Highway System Improvement Program, and the National Highway Performance Program (NHPP) are just some of the existing Federal-aid apportioned programs for which changes in funding, eligible projects, eligible entities and federal shares, among other provisions, are being made.
Other new discretionary programs are established for significant infrastructure programs and freight, equity, planning and project delivery. Research, development, technology and education (RDT&E) program funding levels are authorized with various highway research set-asides established to support deployment and operation of innovative technologies to pilot road usage fees, accelerate digital construction management systems, and advance mobility programs.
The BiL has been characterized as a “once in a generation investment in infrastructure.” As with prior Federal transportation spending bills, the BiL contains provisions that can be expected to influence the nation’s economic competitiveness, environmental sustainability and development priorities. In this case, the BiL offers new opportunities for planning, building, and maintaining a transportation system that is more reliable and safe, equitable, and resilient to economic and energy security challenges and climate change.
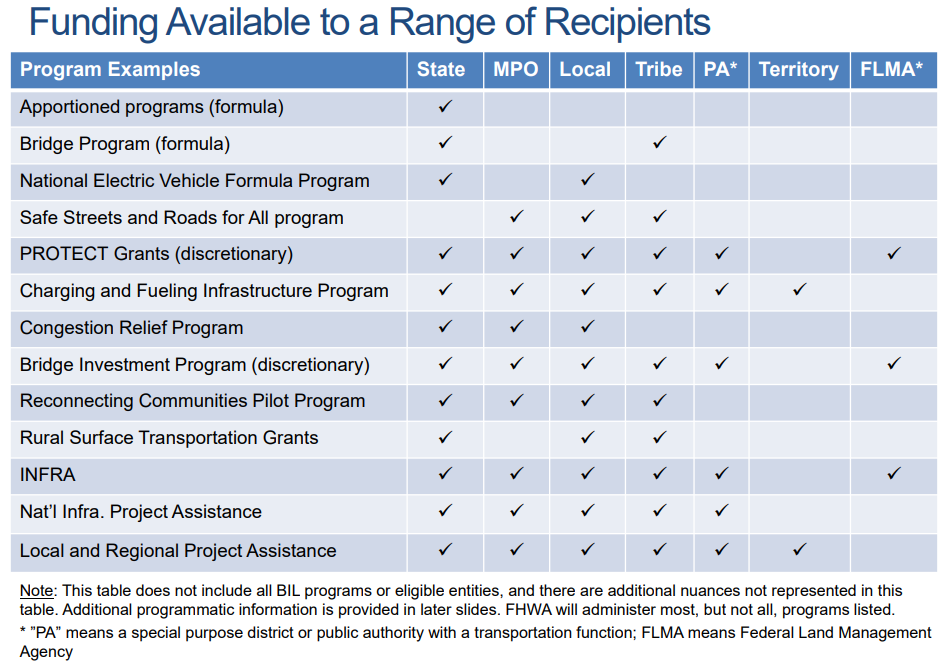
RESOURCES
Referenced Resources:
[1] Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL) * Overview of Highway Provisions file
[2] The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law Will Deliver for New Jersey https://www.transportation.gov/briefing-room/bipartisan-infrastructure-law-will-deliver-new-jersey
[3] Justice40 Initiative https://www.transportation.gov/equity-Justice40
[4] Distribution of Promoting Resilient Operations for the Transformative, Efficient, and Cost-Saving Transportation (PROTECT) Program Funds Apportioned for Fiscal Year 2022 https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/legsregs/directives/notices/n4510864/n4510864_t20.cfm
[5] NJ will receive $15.4 million to expand electric vehicle charging infrastructure this year https://dailytargum.com/article/2022/02/nj-will-receive-usd15-4-million-to-expand-electric-vehicle-charging
Other Resources Highlighted:
- Safe Streets and Roads for All (SS4A) Grant Program. https://www.transportation.gov/grants/SS4A
- Complete Streets in FHWA. https://highways.dot.gov/complete-streets/complete-streets-fhwa
- FHWA Issues New Highway Safety Funding Guidance. https://aashtojournal.org/2022/02/04/fhwa-issues-new-highway-safety-funding-guida
- Justice40 Initiative. https://www.transportation.gov/equity-Justice40/
- Reconnecting Communities Pilot Program – Planning Grants and Capital Construction Grants. https://www.transportation.gov/grants/reconnecting-communities
- Carbon Reduction Program (CRP). https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/bipartisan-infrastructure-law/crp_fact_sheet.cfm
- Get Ready to Apply for PROTECT Resilience Grants. https://www.nlc.org/article/2022/05/09/get-ready-to-apply-for-protect-resilience-grants/
- President Biden, USDOT and USDOE Announce $5 Billion over Five Years for National EV Charging Network, Made Possible by Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. https://www.transportation.gov/briefing-room/president-biden-usdot-and-usdoe-announce-5-billion-over-five-years-national-ev
- Federal Funding Programs. https://www.transportation.gov/rural/ev/toolkit/ev-infrastructure-funding-and-financing/federal-funding-programs
- NJ will receive $15.4 million to expand electric vehicle charging infrastructure this year. https://dailytargum.com/article/2022/02/nj-will-receive-usd15-4-million-to-expand-electric-vehicle-charging
- Bipartisan Infrastructure Law Fact Sheets. https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/bipartisan-infrastructure-law/fact_sheets.cfm

