
Jan 3, 2025 | Innovation Interview, News, Peer Exchange
For over 45 years, the Transportation Pooled Fund (TPF) Program has made it possible for public and private entities to combine resources for high‑priority transportation research. By pooling funds and expertise, participating organizations can support research that...

Oct 18, 2024 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, News
Wildlife crossings help to bridge greenspaces divided by roads, streets, and highways through the creation of safe alternative pathways for wildlife. For the past forty years, wildlife crossings have been a part of New Jersey’s transportation network. The state’s...
May 13, 2024 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, News, Research Project, Research Showcase, Research Spotlight
Concrete production is energy intensive, and requires materials that are both challenging, and expensive to acquire. Material engineers are seeking alternative materials that are more cost-effective and carbon-friendly, but also operate successfully as road and...

Apr 2, 2024 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, News, Research Project, Research Spotlight
Biometric sensors have long been used in cognitive psychology to measure the stress-level of individuals. These sensors can measure a variety of human behaviors that translate as stress: the movement of eyes, stress-induced sweat, and heart rate variability. Recently,...
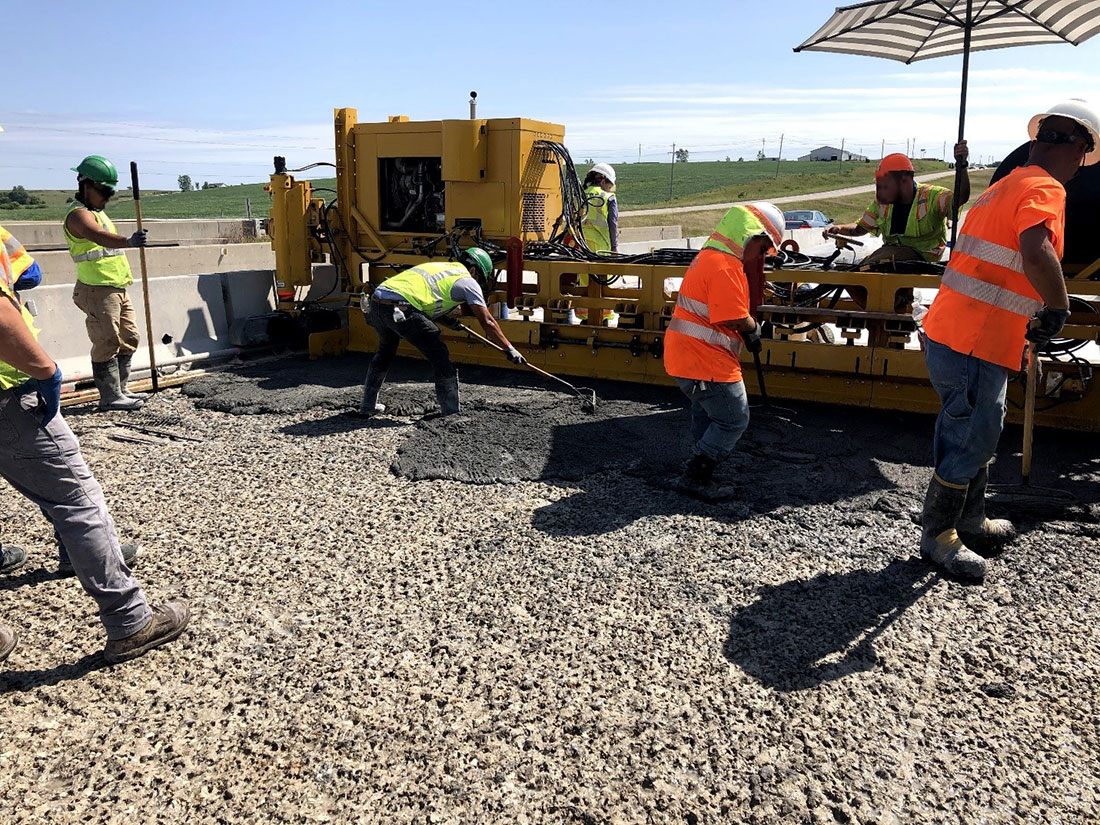

Feb 13, 2024 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, Innovative Initiative, News, Research Spotlight
UHPC for Bridge Preservation and Repair is a model innovation that was featured in FHWA’s Every Day Counts Program (EDC-6). UHPC is recognized as an innovative new material that can be used to extend the life of bridges. Its enhanced strength reduces the need for...

Feb 7, 2024 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, Innovative Initiative, News
Enhancing Performance with Internally Cured Concrete (EPIC2) is a model innovation in the latest round of the FHWA’s Every Day Counts Program (EDC-7). EPIC2 is recognized as an innovative new technique that can be used to extend the life of concrete bridges and roads....










