
Sep 7, 2023 | Innovation Spotlight, Innovative Initiative, News, NJ STIC, Online Learning
The New Jersey Department of Transportation’s Traffic Incident Management (NJTIM) training is now available as an online, self-guided course. Bringing first responder training program to an online training platform should make it easier for even more emergency and...

Jul 20, 2023 | Innovative Initiative, News, Online Learning
The Federal Highway Administration’s (FHWA) Talking TIM webinar series provides best practices, new technological innovations, and successful implementations. The webinar series provides a forum where TIM champions with any level of experience can exchange...
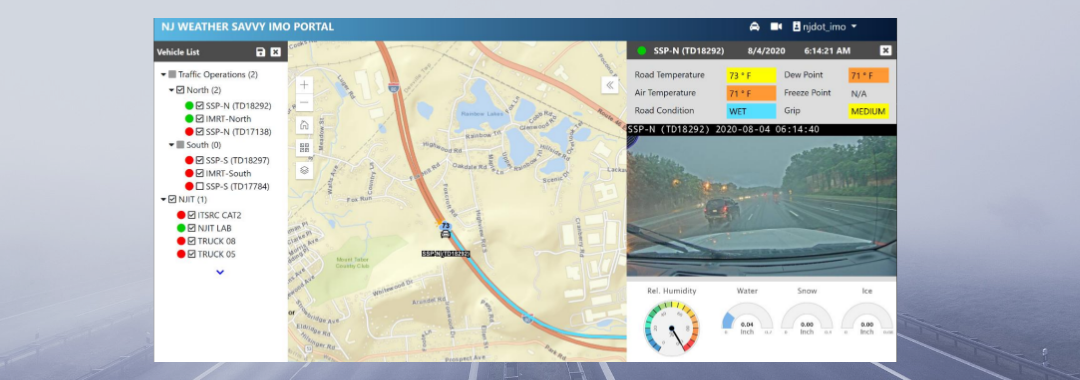
Feb 10, 2022 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, Innovative Initiative, News, NJ STIC
NJDOT’s Transportation Mobility unit is working on several initiatives related to FHWA Every Day Counts innovative initiatives, including: Crowdsourcing for Advancing Operations (EDC-4, EDC-6), Next Generation Traffic Incident Management (EDC-4, EDC-6), and...

Jun 10, 2021 | Innovation Interview, Innovation Spotlight, Innovative Initiative, News, NJ STIC
Traffic Incident Management (TIM) programs help first responders and traffic operators to better understand and coordinate roadway incidents. As part of the sixth round of the Federal Highway Administration’s (FHWA) Every Day Counts (EDC) initiative, the agency...

Oct 19, 2020 | News, NJ STIC
NJDOT’s New Jersey’s Traffic Incident Management (TIM) program consists of a planned and coordinated multi-disciplinary process to detect, respond to, and clear traffic incidents so that traffic flow may be restored as safely and quickly as possible after an incident....









